- RWM structure
-
It is critical to understand the round window membrane-RWM structure in order to design proper delivery methods across RWM. Some of the important features that have not been reported previously:
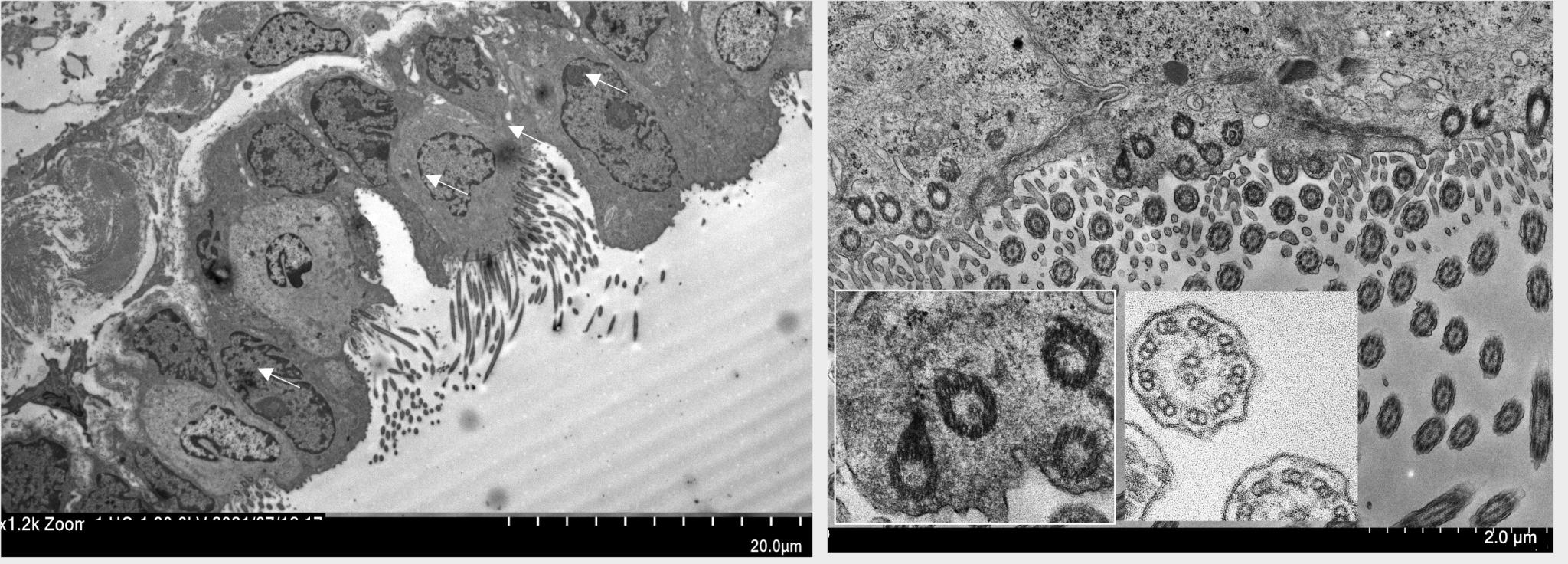
1. RWM outer epithelial layer entails cilia with 9+2 microtubule structure shown in the porcine RWM transmission electron microscopy-TEM micrograph below; each ciliated cell is supported by two non-ciliated cells (pointed by white arrows):
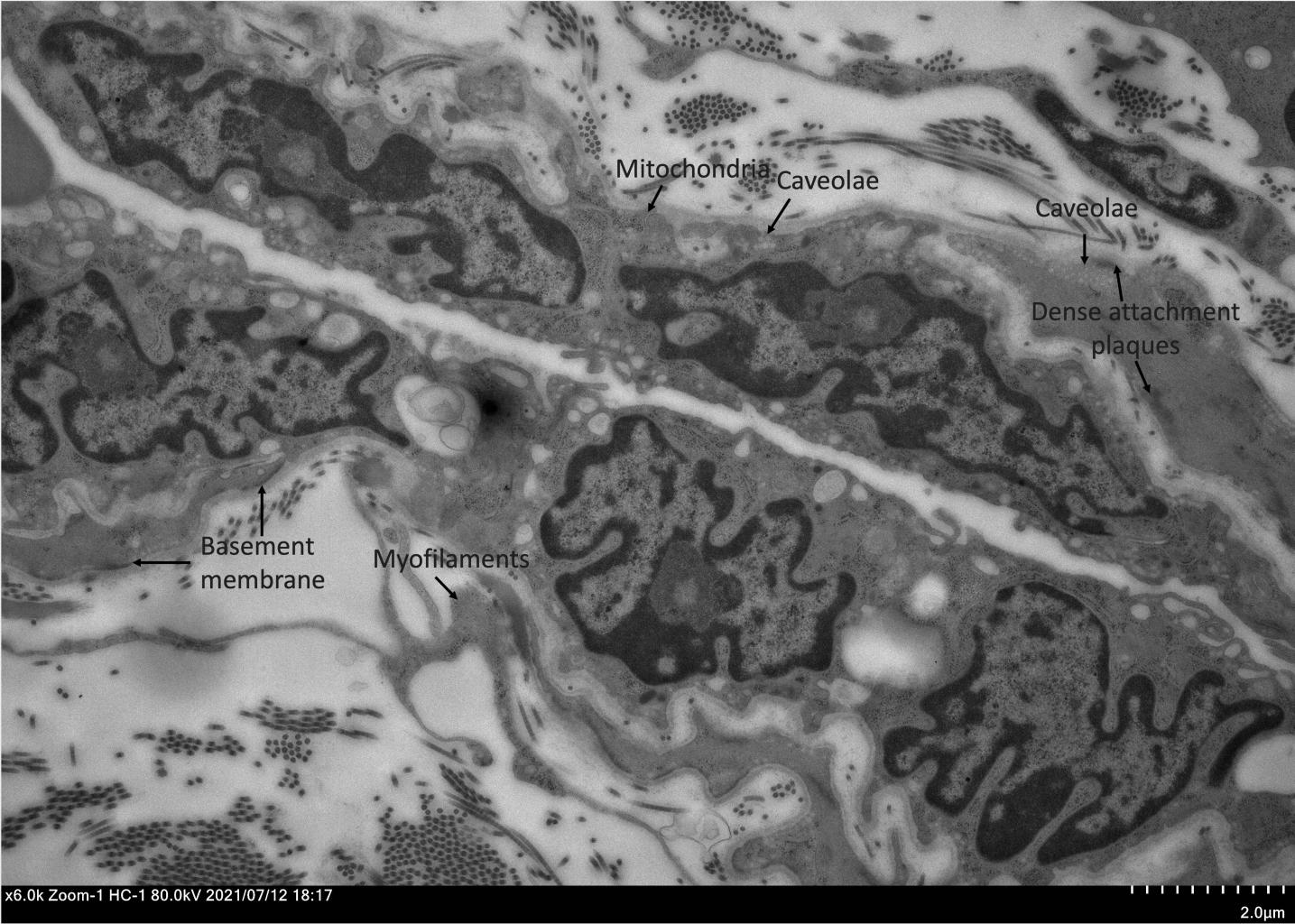
2. RWM middle fibroblastic layer possibly entails smooth muscle cells shown in the porcine RWM TEM micrograph below:
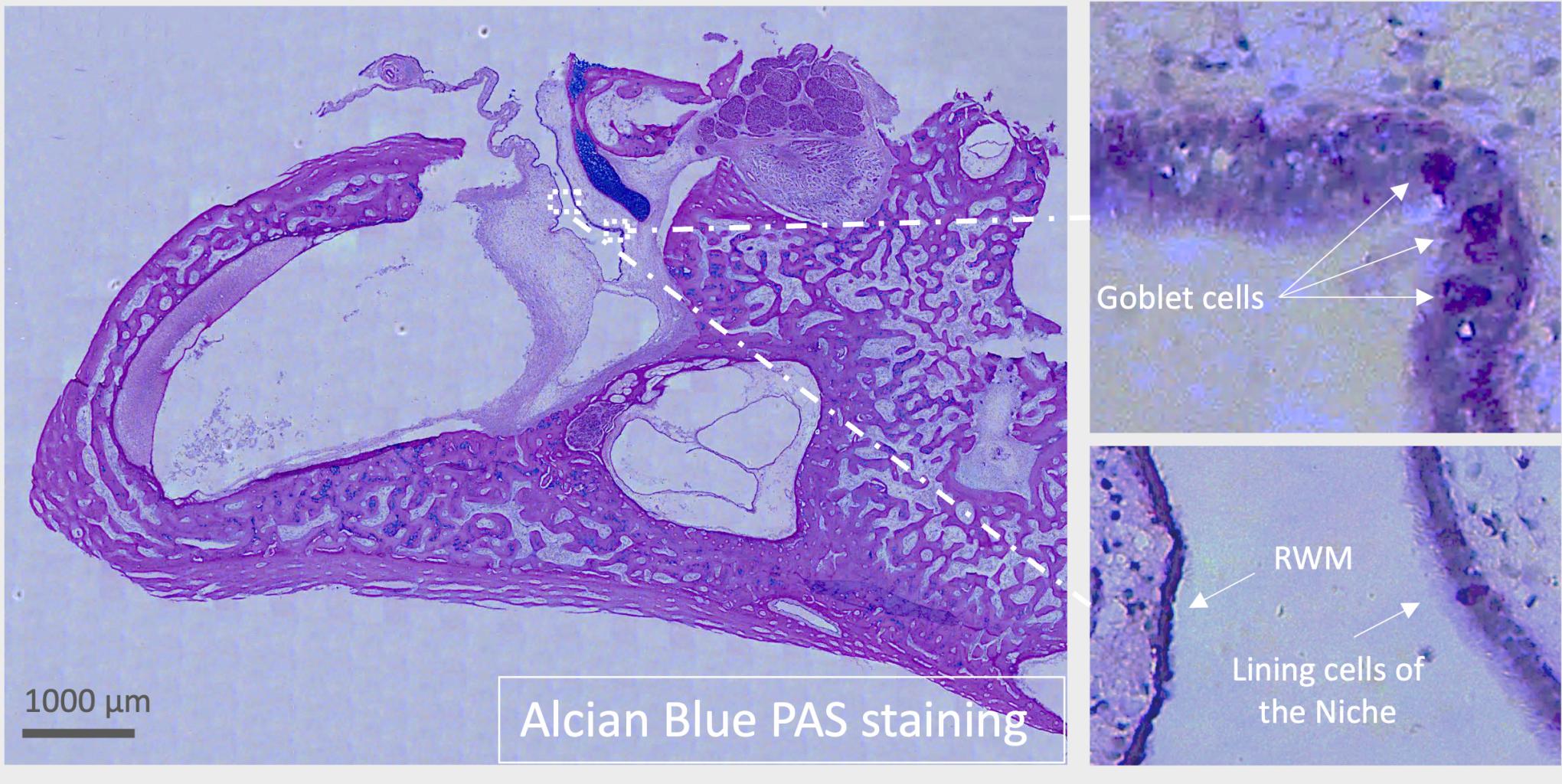
3. RW niche entails goblet cells that release mucus shown in the porcine inner ear section (5 um) below:
- RWM sensory receptors
-
One of our goal is identifying novel sensory receptors and channels of round window membrane that sense chemicals, investigating how receptors and channels regulate drug passage to the inner ear, and harnessing receptors and channels to improve inner ear drug delivery.
For example we identified G-protein-coupled taste receptors in the porcine RWM cells.
One of the important factors that affect the drug half-life is the taste of the drug and their interaction with G-protein-coupled taste receptors. Bitter receptors, in particular, trigger the release of NO in response to bitter and bacterial compounds, which enhances mucociliary clearance by increasing ciliary beat frequency; sweet receptor stimulation inhibits bitter receptor response, demonstrating an antagonistic interaction. This would make the RWM entry a chemosensory and a mucosal rout rather than a simple membrane.
The RWM outer epithelial layer entails ciliary structure equipped with localized bitter taste receptors that interacts with drugs. We have successfully improved the half-life of drugs by inhibiting these receptors in pigs.
Live confocal imaging of the interaction of dexamethasone fluorescein (DexF) with mouse RWM epithelial layer:
The optical coherence tomography-OCT recording shows the activated mucociliary transport at gerbil RW niche after 2 min application of dexamethasone fluorescein (DexF); the diagonal white line is the RWM:
