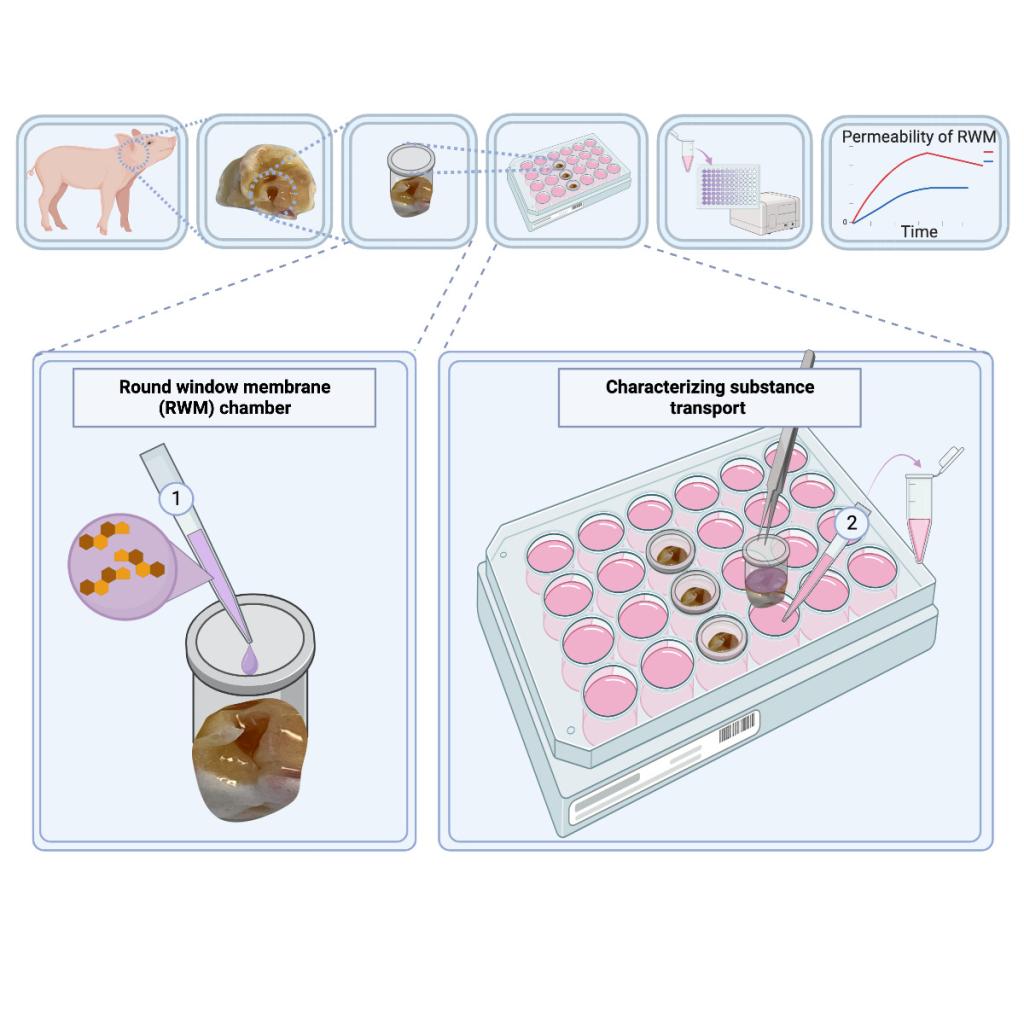
- ex-vivo model
-
Delivery of pharmaceutical therapeutics to the inner ear to treat and prevent hearing loss is challenging. Systemic delivery is not effective as only a small fraction of the therapeutic agent reaches the inner ear. Invasive surgeries to inject through the round window membrane (RWM) or cochleostomy may cause damage to the inner ear. An alternative approach is to administer drugs into the middle ear using an intratympanic injection, with the drugs primarily passing through the RWM to the inner ear. However, the RWM is a barrier, only permeable to a small number of molecules. To study and enhance the RWM permeability, we developed an ex vivo porcine RWM model, similar in structure and thickness to the human RWM. The model is viable for days, and drug passage can be measured at multiple time points. This model provides a straightforward approach to developing effective and non-invasive delivery methods to the inner ear.
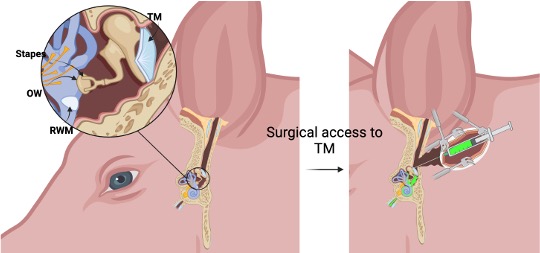
- in-vivo model
-
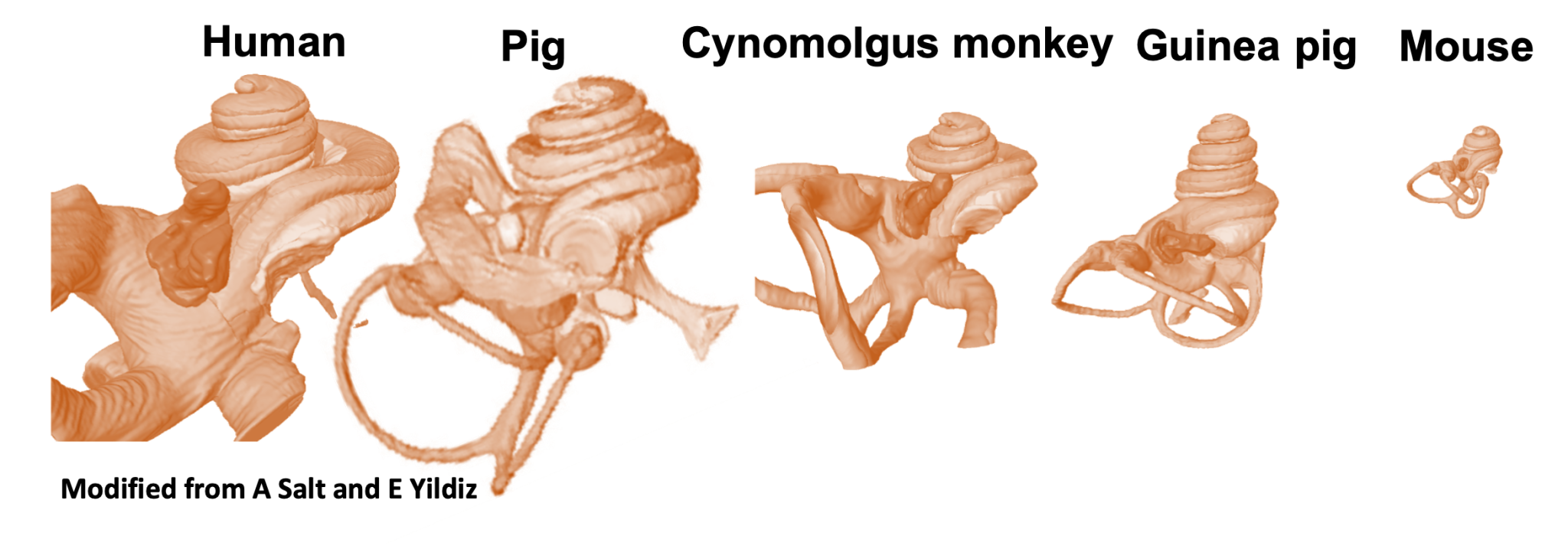
One major obstacle in validating drugs for the treatment or prevention of hearing loss is the limited data available on the distribution and concentration of drugs in the human inner ear. Although small animal models offer some insights into inner ear pharmacokinetics, their smaller organ size and different barrier (round window membrane) permeabilities compared to humans can complicate study interpretation. Therefore, developing a reliable large animal model for inner ear drug delivery is crucial. The inner and middle ear anatomy of domestic pigs closely resembles that of humans, making them promising candidates for studying inner ear pharmacokinetics. However, unlike humans, the anatomical orientation and tortuosity of the porcine external ear canal frustrates local drug delivery to the inner ear. We developed a surgical technique to access the tympanic membrane of pigs. To assess hearing pre- and post-surgery, auditory brainstem responses to click and pure tones are measured.
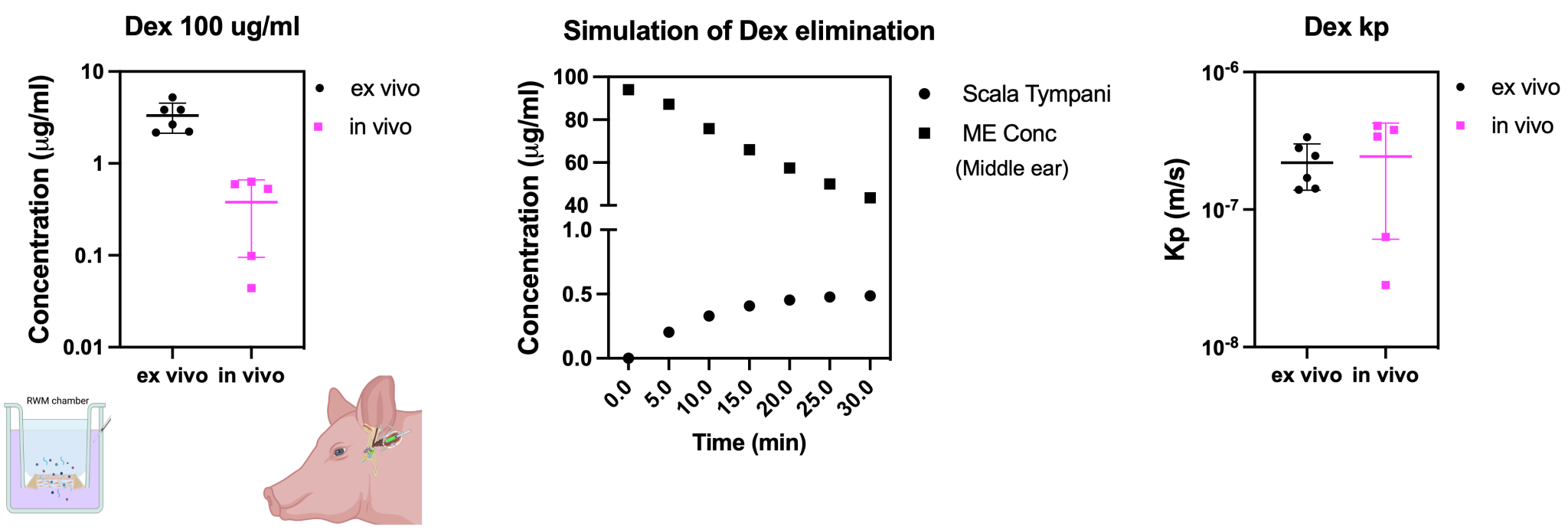
- Comparing ex-vivo vs in-vivo data
-
As the ex-vivo chamber cannot take into the account the middle ear drug kinetics and loss through the euchastian tube, the combination of ex-vivo data and simulation (Fluidsim) of middle kinetics together yield accurate results comparable to in-vivo data.
- Dexamethasone (Dex) 100 ug/ml via intratympanic injection
- Perilymph sampling from RWM
- Kp: permeability
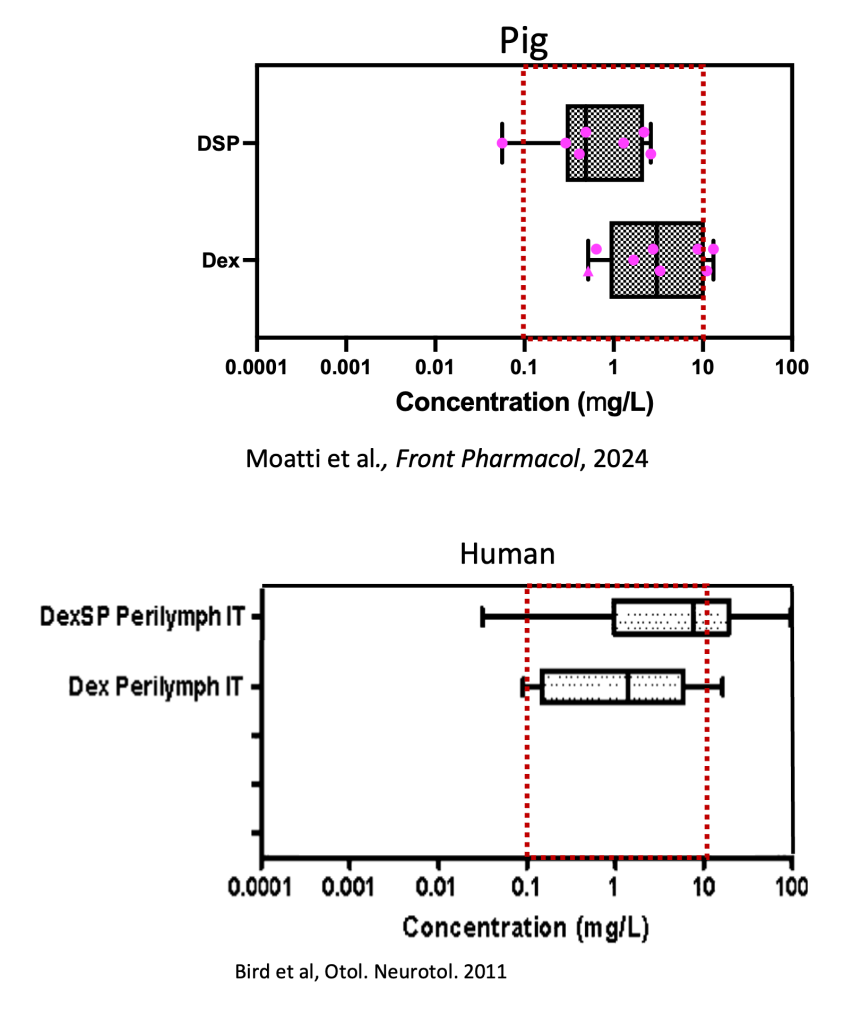
- Comparing pig vs human data
-
The Human versus pig intratympanic delivery of dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP) is comparable.
- Dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP) 4 mg/ml via intratympanic injection
- Perilymph sampling from RWM
- mean (DSP + Dex): 6.3 versus 8.9 µg/mL